Introduction: Why Understanding How AI Works Matters in 2026
Artificial Intelligence has become the backbone of modern technology, and in 2026, it is no longer a futuristic concept—it is part of almost everything we use daily. From the apps in your smartphone to the tools businesses rely on, AI is silently driving decisions, automating tasks, and improving accuracy. Because AI is now shaping industries, jobs, creativity, and even personal productivity, understanding how AI works is no longer optional. It’s becoming a basic digital skill, just like using the internet or a smartphone.
In 2026, millions of people will rely on AI tools without knowing what happens behind the scenes. We ask AI chatbots for help, use AI-generated images, trust how AI works in navigation apps, and depend on AI-powered health systems. But without understanding the fundamentals, it’s easy to develop misconceptions—such as thinking AI is “human-like,” “magical,” or “dangerous.” The truth is simple: AI is a powerful mathematical and data-driven system, not a human brain. Learning how AI works helps remove fear, confusion, and unrealistic expectations.
Understanding how AI works also matters because employers now value AI literacy. Businesses across marketing, finance, healthcare, education, and e-commerce expect people to know at least the basics of AI. When you know how AI processes data, how it learns patterns, and how it makes predictions, you become better at using these tools effectively and safely. You also gain the ability to spot errors, biases, or limitations in AI-generated results.
Finally, as how AI works becomes more advanced, individuals who understand its working principles will have a major advantage—whether they’re students, professionals, entrepreneurs, or content creators. Knowing how AI operates empowers you to use it smarter, adopt it earlier, and future-proof your skillset. In short, learning how AI works in 2026 is essential for staying relevant, informed, and ahead of the curve.

2. What Does AI Really Do? A Beginner-Friendly Breakdown
Artificial Intelligence can feel complicated, but at its core, how AI works is simply a technology that helps machines perform tasks that normally require human intelligence. These tasks include understanding language, recognizing images, making predictions, solving problems, and even learning from past experiences. In simple words, AI helps computers think, learn, and act in a smart and efficient way.
To understand how AI really works, imagine teaching a child. You give examples, show patterns, correct mistakes, and over time, the child learns to recognize things and make better decisions. AI works the same way. It receives large amounts of data, learns patterns inside that data, and makes predictions based on what it has learned. The more data it gets, the better it becomes. This process is called machine learning, and it is the foundation of modern AI.
One of the biggest strengths of AI is its ability to analyze huge amounts of information very quickly—much faster than any human. For example, when Netflix recommends a movie, it analyzes your watching history, compares it with millions of other users, and instantly suggests something you’re likely to enjoy. When Google Maps predicts traffic, it processes real-time signals from thousands of devices. When a smartphone improves your photos automatically, AI is identifying faces, colors, and lighting conditions to generate the best result.
AI also helps in understanding human language through Natural Language Processing (NLP). This is how chatbots, virtual assistants, and translation apps work. When you type or speak, AI breaks down your words, understands the context, and provides the best possible answer. This is why in 2026, tools like voice assistants, AI writing tools, and customer support bots have become incredibly advanced and natural.
Another important function of how AI works is computer vision, which allows machines to “see” and understand images or videos. Whether it’s identifying a cat in a photo, scanning your face to unlock your phone, or analyzing medical scans for early disease detection, how AI works plays a major role behind the scenes.
AI also excels at prediction. It can forecast stock movements, recommend business decisions, predict customer behavior, detect fraud, and assist doctors in identifying health risks. These predictions are based on analyzing patterns in large datasets that humans cannot manually process.
Overall, AI doesn’t “think” like a human, nor does it replace human intelligence. Instead, it augments human abilities by handling repetitive tasks, analyzing large data, and providing fast, accurate insights. In 2026, understanding what AI does helps people use it more effectively and confidently. Whether you are a student, freelancer, business owner, or everyday user, knowing how AI operates gives you a powerful advantage in a world that is becoming more automated and data-driven every day. According to IBM’s official AI guide, artificial intelligence works by combining large datasets with fast processing and smart algorithms. https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/what-is-artificial-intelligence

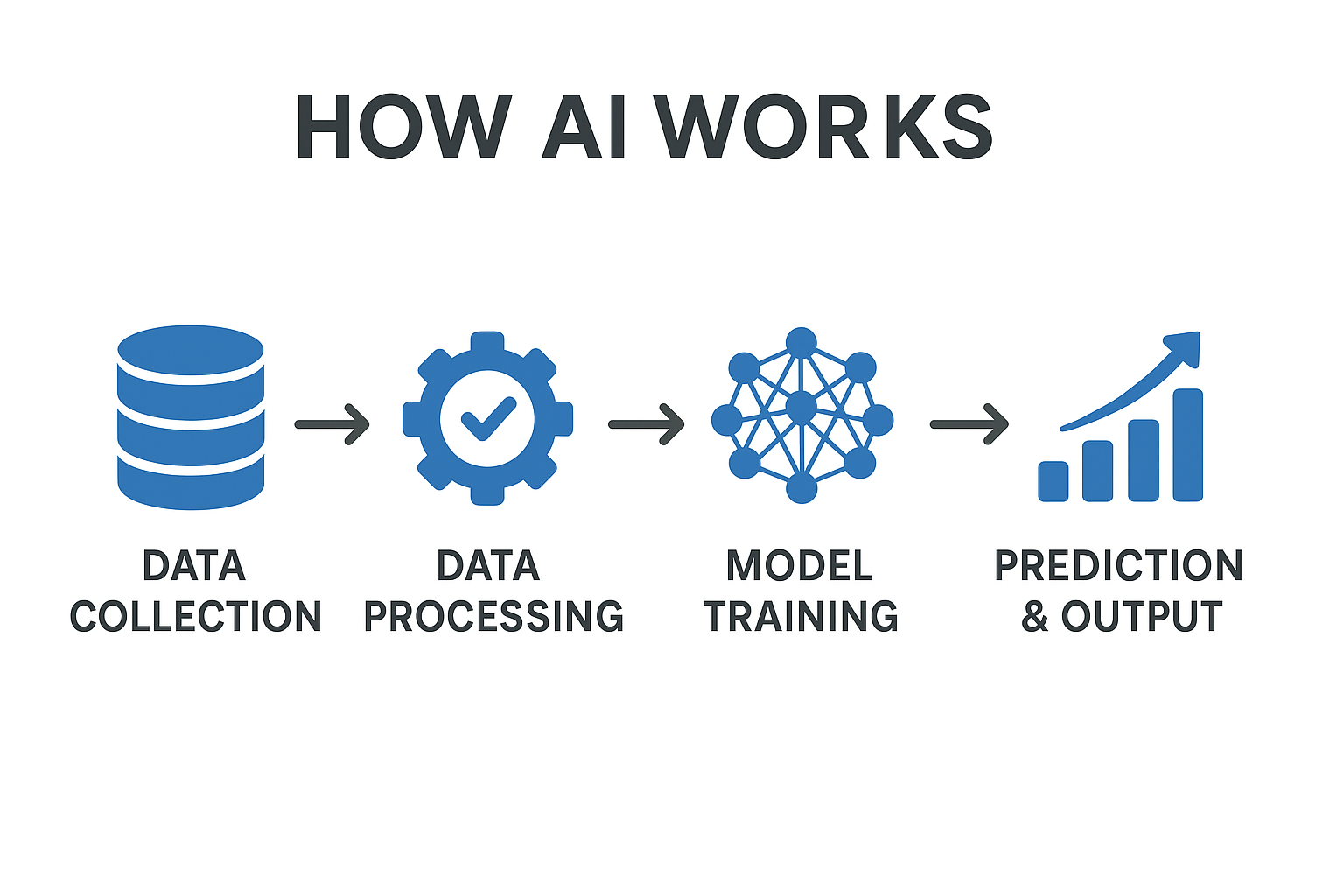
How AI Works (Explained Simply)
Understanding how AI works becomes easy when you break it down into simple steps. At its core, AI follows a clear process: it takes data, learns patterns from that data, makes decisions or predictions, and improves over time through feedback. This entire cycle is what gives AI its “intelligence.”
The first stage is data input. AI cannot think on its own—it needs information. This information can be in the form of text, images, voice recordings, numbers, or even real-time signals. For example, an AI model trained to recognize cats needs thousands of pictures of cats. A chatbot needs millions of sentences to learn how humans communicate. The quality and quantity of this data directly affect how well the AI performs.
Next comes learning, which is the heart of AI and how AI works. This learning process is done through something called machine learning. As explained by MIT, machine learning allows computers to learn patterns without being explicitly programmed. https://mitsloan.mit.edu/ideas-made-to-matter/machine-learning-explained Instead of being programmed with fixed instructions, the AI “learns” from patterns in the data. For instance, one might notice that cats often have pointed ears, whiskers, and similar shapes. Over time, it forms rules based on these patterns—rules that humans don’t need to write manually.
The third step is prediction or decision-making. Once how AI works learns, it can start making predictions. For example, when you upload a photo, AI can instantly decide whether it contains a cat. When you ask a chatbot a question, AI predicts the best possible answer based on millions of examples it has seen during training.
Finally, there is the feedback loop. AI improves itself by comparing its predictions with the correct answers and adjusting its internal rules. This self-improvement makes AI more accurate over time, just like how humans learn from mistakes.
In simple words, how AI works by learning from data, recognizing patterns, and making smart decisions—but all based on math, not magic.

How AI Works in Simple Words (For Absolute Beginners)
Understanding how AI works doesn’t require any technical background. In the simplest words, Artificial Intelligence is like a very fast learner that studies examples, remembers patterns, and uses those patterns to make predictions or decisions. It doesn’t think like a human, doesn’t have feelings, and doesn’t understand the world the way we do. It only works with the data we give it. Google’s AI Blog shows how modern AI models use neural networks for better decision-making.
Let’s break this down using an easy example. Imagine you want to teach a child how to recognize an apple. You show the child many pictures—red apples, green apples, apples hanging from trees, apples sliced in half. After seeing hundreds of apples, the child begins to understand the common features: round shape, certain colors, a stem, and a shiny surface. Now, when you show a new picture, the child can say, “That’s an apple.” AI learns in exactly the same way.
AI begins with data. Data is simply information—images, words, numbers, voice recordings, or anything that can be stored digitally. To teach AI something, you give it a lot of this data. For example, if the goal is to help AI understand language, you feed it millions of sentences. If the goal is to help AI recognize dogs, you give it thousands of dog photos. The more data the AI sees, the more accurate it becomes.
Once AI receives the data, it starts the process of learning patterns. This learning happens through techniques like machine learning and deep learning, but even these advanced methods follow a simple idea: the AI looks for repeated patterns. If it sees that dogs usually have four legs, a tail, and certain face shapes, it stores that information. If it sees that polite sentences often include words like “please” or “thank you,” it stores that pattern too. AI becomes smarter as it identifies these patterns.
After learning, AI begins to make predictions. When you take a photo and your smartphone labels it as “dog,” the AI is predicting that the pattern in your image matches the patterns it learned. When a chatbot responds to your question, it predicts the most helpful answer based on patterns in millions of conversations. These predictions may look magical, but they are simply the result of a machine matching patterns and calculating the best outcome.
One of the most powerful aspects of AI is that it continues to improve through feedback. When AI makes a mistake, developers correct it, users give feedback, or the system compares its prediction to the correct answer. This correction helps it refine its patterns. Over time, it becomes more accurate, faster, and more reliable. This is why AI tools in 2026 feel much more intelligent than earlier versions—they have learned from billions of real-world examples.
In very simple words:
AI is a pattern-learning machine. It learns from examples, finds similarities, and makes predictions based on what it has learned.
It’s not magic—it’s mathematics, data, and practice working together at incredible speed.

The Core Technologies Behind How AI Works
Artificial Intelligence may look like one big advanced technology, but in reality, it is built on several core technologies working together. These technologies give AI the ability to learn, analyze, understand language, and even “see” the world. Understanding these foundations helps beginners see that AI is not magic—it’s a combination of smart algorithms and data-driven processes. The four most important technologies behind AI are Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Computer Vision.
5.1 Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning is the backbone of modern AI. It allows computers to learn from data without being programmed with step-by-step instructions. Instead of telling the computer what to do, we give it examples and let it find patterns.
For example, in a spam filter, the algorithm studies thousands of emails labeled as “spam” and “not spam.” Over time, it recognizes patterns—specific words, links, or behaviors—and predicts which new messages should be filtered. Machine Learning powers recommendation systems (like Netflix), fraud detection systems, pricing algorithms, and much more. ML models improve with more data, making them smarter and more accurate over time.
5.2 Deep Learning (DL)
Deep Learning is a special type of Machine Learning inspired by how the human brain works. It uses structures called neural networks, which are layers of interconnected nodes that process data. Deep Learning models can learn extremely complex patterns, especially in images, audio, and large text datasets.
This technology powers image recognition, voice assistants, autonomous driving systems, and advanced generative AI like ChatGPT and image generators. Deep Learning works so well because it can automatically learn rich features from raw data—something older algorithms could not do. The more layers it has, the deeper and more powerful the model becomes.
5.3 Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP is the technology that allows AI to understand, interpret, and generate human language. This is what makes chatbots, voice assistants, translation tools, and email smart replies possible. NLP breaks down human language into smaller pieces—words, grammar, tone, and context—to understand meaning.
Modern NLP models in 2026 can handle complex tasks, like writing articles, answering questions, analyzing emotions, summarizing long texts, and speaking almost like humans. NLP makes AI communication smooth, natural, and useful in daily life.
5.4 Computer Vision (CV)
Computer Vision gives machines the ability to “see” and interpret images or videos. This technology identifies objects, faces, places, and even emotions in visual content. It works by analyzing pixels and patterns, then comparing them to what it has learned from previous examples.
Computer Vision powers facial recognition, medical imaging scans, self-driving cars, CCTV analysis, mobile cameras, and even quality checks in factories. In 2026, CV has become extremely accurate due to massive image datasets and powerful training methods.

How AI Works in Everyday Life (Real Examples 2026)
Artificial Intelligence has become so deeply integrated into our everyday lives that most people use it dozens of times a day without even realizing it. In 2026, AI is no longer a specialized technology used only by tech experts. It is quietly powering smartphones, businesses, healthcare systems, transportation, education, and even household devices. Understanding how AI works in daily life helps you see its real-world impact and why it has become such an essential part of modern living.
AI in Smartphones
Every smartphone today is packed with AI features. When you unlock your phone using Face ID, AI uses computer vision to scan and analyze your facial features in milliseconds. When you take a picture, the camera enhances lighting, removes noise, and adjusts colors using machine learning models that understand what makes a good photo. Even your typing is AI-assisted—predictive text and autocorrect learn your writing style and become more accurate over time.
Apps like Google Assistant, Siri, and chatbot-based tools use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand voice commands, answer questions, set reminders, or translate language instantly. In short, AI makes your phone smarter, more responsive, and more personal.
AI in Healthcare
In 2026, healthcare has undergone a major transformation because of AI. Machine learning models can analyze medical images—like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans—with incredible accuracy. These systems help doctors detect diseases earlier and more accurately than ever before.
AI also assists in diagnosing symptoms, predicting risks of illness, creating personalized treatment plans, and monitoring patients remotely. Wearable devices use AI to track heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity, alerting you to potential health issues before they become serious.
AI in Call Centers & Customer Service
If you’ve ever chatted with a support bot or used a voice helpline, you’ve used AI. Modern companies rely on advanced AI chatbots that understand complex questions, solve problems instantly, and respond just like human agents. These bots use NLP to understand customer messages and Machine Learning to provide accurate solutions.
AI also listens to customer calls, analyzes tone, and provides real-time suggestions to human agents to improve service quality.
AI in Shopping & E-Commerce
Whether you shop on Amazon, Daraz, Alibaba, or any e-commerce site, AI is constantly working in the background. It recommends products based on your browsing history, predicts what you might want to buy next, and even adjusts prices dynamically.
AI also detects fraud, manages inventory, and helps sellers understand customer behavior. In 2026, AI-driven product descriptions, image generation, and ads have become standard tools for online sellers.
AI in Daily Life & Smart Homes
Smart home devices like Alexa, Google Home, smart bulbs, and thermostats use AI to learn your routines. They can turn on lights when you arrive, adjust temperature automatically, remind you of tasks, and control appliances through voice commands.
Even your car uses AI—navigation apps predict traffic, self-driving features assist in braking and lane control, and sensors monitor road safety in real time.
In simple words:
AI is everywhere—helping you shop, improving your health, guiding your travel, powering your phone, enhancing customer service, and making daily life easier. In 2026, AI has become an invisible assistant that works silently in the background, increasing convenience, accuracy, and efficiency in everything you do.

How AI Works With a Diagram (Simple Visual Explanation
Understanding how Artificial Intelligence works can feel confusing, especially because the technology behind it is vast and complex. But at its core, AI follows a very simple flow: it takes data, learns patterns, makes decisions, and improves over time. To make this easier, here is a simple diagram followed by a detailed explanation of each step.

Step-by-Step Explanation of How AI Works
AI may seem like a black box from the outside, but its functioning is quite systematic. Let’s break down the process in simple, understandable terms that reflect how modern AI works as of 2026.
1. Input: Where Everything Begins
AI systems need input data to function. This data can be anything: photos, voice recordings, text messages, numbers from sensors, videos, or even user questions. Without data, AI has nothing to analyze or learn from. In 2026, AI models are trained using massive and diverse datasets, which help them understand human language, recognize patterns, and operate across multiple domains.
2. Preprocessing: Cleaning and Organizing Data
Raw data is often messy. It contains errors, missing values, duplicates, or irrelevant information. Before feeding it into an AI model, the data must be:
Why numbers? Because computers understand mathematics, not words or images. So images become pixel values, text becomes tokens, and audio becomes waveforms.
This step ensures that the model receives high-quality, usable data.
3. Model Training: Learning the Patterns
Training is the heart of AI. During training, the model is shown large amounts of data and learns to identify patterns. For example:
-
To learn language → it sees billions of sentences
-
To recognize cats → it analyzes thousands of cat images
-
To understand speech → it listens to audio samples
The model adjusts its internal mathematical parameters (called weights) using algorithms like gradient descent. This process continues until the model becomes good at predicting or generating the correct result.
In 2026, training uses advanced neural architectures, huge GPU clusters, and techniques like reinforcement learning and multimodal learning.
4. The AI Model: Ready to Work
Once training is complete, the AI model becomes capable of:
-
Answering questions
-
Translating languages
-
Creating text and images
-
Detecting objects
-
Predicting outcomes
-
Analyzing data
This trained model does not “think” like humans. Instead, it calculates probabilities based on patterns learned during training.
5. Output: The Final Result
The final stage is the output. Depending on the use case, the output might be:
The output may then feed back into the system for further improvement, creating a feedback loop that helps AI evolve over time.
In Simple Words: AI = Patterns + Math + Data
This diagram and workflow show that AI is not magic. It is a system built on structured steps that convert data into intelligent behavior. By understanding this flow, anyone can appreciate how AI tools work behind the scenes and why data quality, model design, and training are so important.
Conclusion: AI Isn’t Magic — It’s Smart Math + Data — How AI Works in 2026
As we reach 2026, Artificial Intelligence has become more powerful and more integrated into our lives than ever before. But despite its rapid progress, one thing remains true: AI isn’t magic — it is the result of smart mathematics, huge datasets, and highly optimized computational systems. Understanding this truth helps us see AI not as something mysterious or uncontrollable, but as a tool built on logic, patterns, and engineering.
In 2026, AI systems still rely on the same foundational building blocks: algorithms that learn patterns from data. What has changed is the scale. Models today are trained on trillions of data points, allowing them to understand language, images, audio, and even complex patterns such as human reasoning at far deeper levels. These models use advanced neural networks, optimized learning architectures, and large-scale parallel computing. This combination enables them to generate human-level text, solve complicated problems, translate languages instantly, create images, and even assist in scientific research.
Another important change in 2026 is the rise of Adaptive Learning Systems. Modern AI doesn’t just learn once and stop — it continuously improves through feedback loops. This means an AI model can refine its accuracy based on how users interact with it, making it more useful over time. Still, this learning process is controlled by strict mathematical rules to ensure safety, reliability, and predictability.
Equally important is the expansion of Multimodal AI. Earlier, most AI systems could understand only one type of input, such as text or images. But in 2026, AI can process and combine multiple types of information at the same time — text, images, audio, video, sensor data, and more. This allows AI to understand the world in a more human-like way. For example, an AI assistant can read a paragraph, analyze a chart, interpret an image, and produce a meaningful answer within seconds.
The year 2026 has also pushed AI beyond simple prediction models. Today’s AI can perform reasoning, break down long instructions, plan multi-step tasks, and explain its decisions more clearly. These capabilities emerge not from any form of consciousness but from deeper mathematical structures, better training data, and smarter optimization techniques.
Finally, the most important shift in 2026 is our understanding of AI. People now recognize that AI is not a replacement for human intelligence, emotions, or creativity. Instead, it is a powerful assistant that amplifies our abilities. Whether it’s helping businesses work faster, supporting doctors, guiding students, or assisting creators, AI’s strength lies in collaboration with humans.
So as you explore the world of AI in 2026, remember this: AI is extraordinary, but not mysterious. It is built from numbers, patterns, probabilities, and logic. The future belongs not to those who fear AI, but to those who understand it and use it wisely.